[문제]
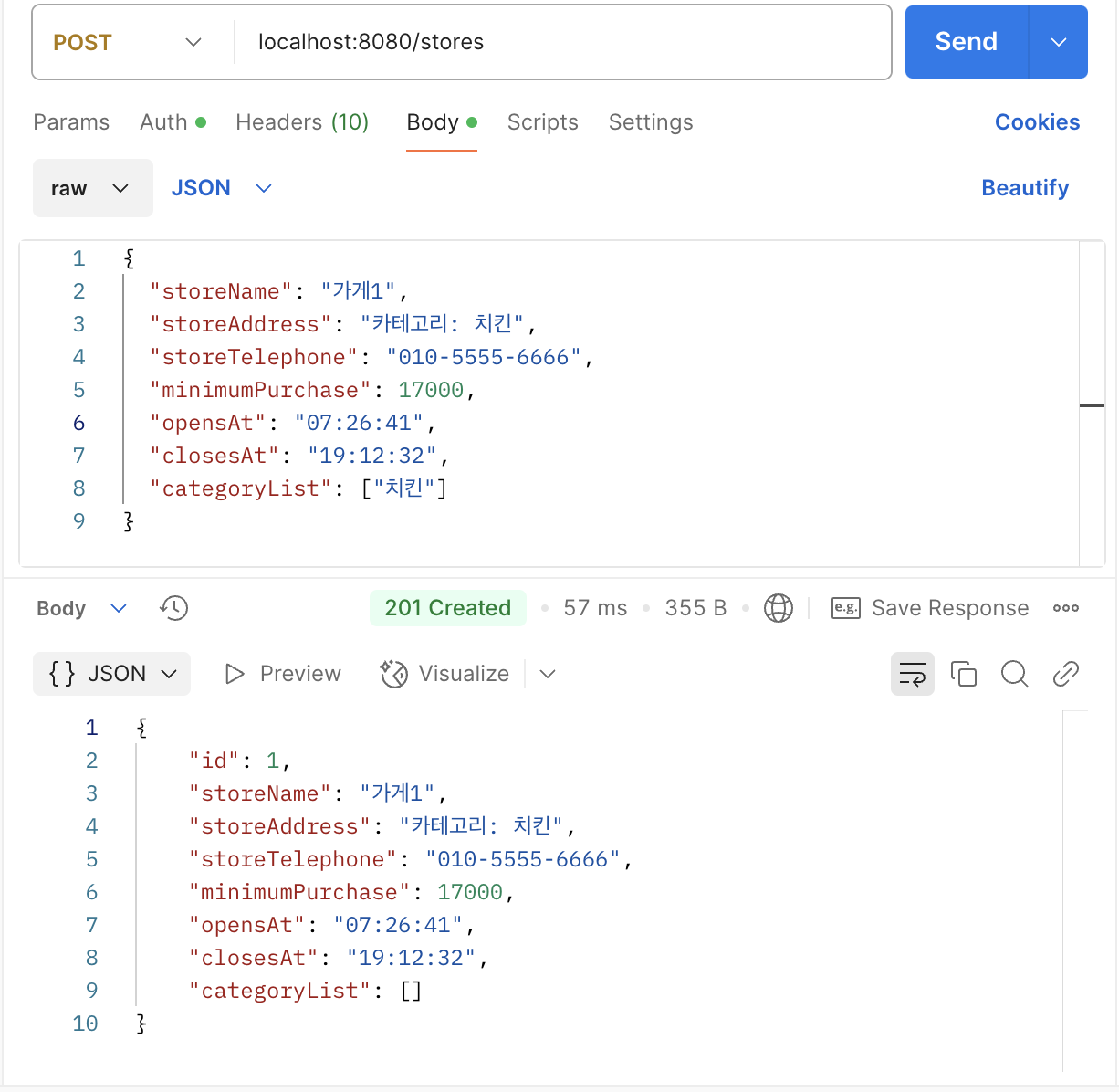
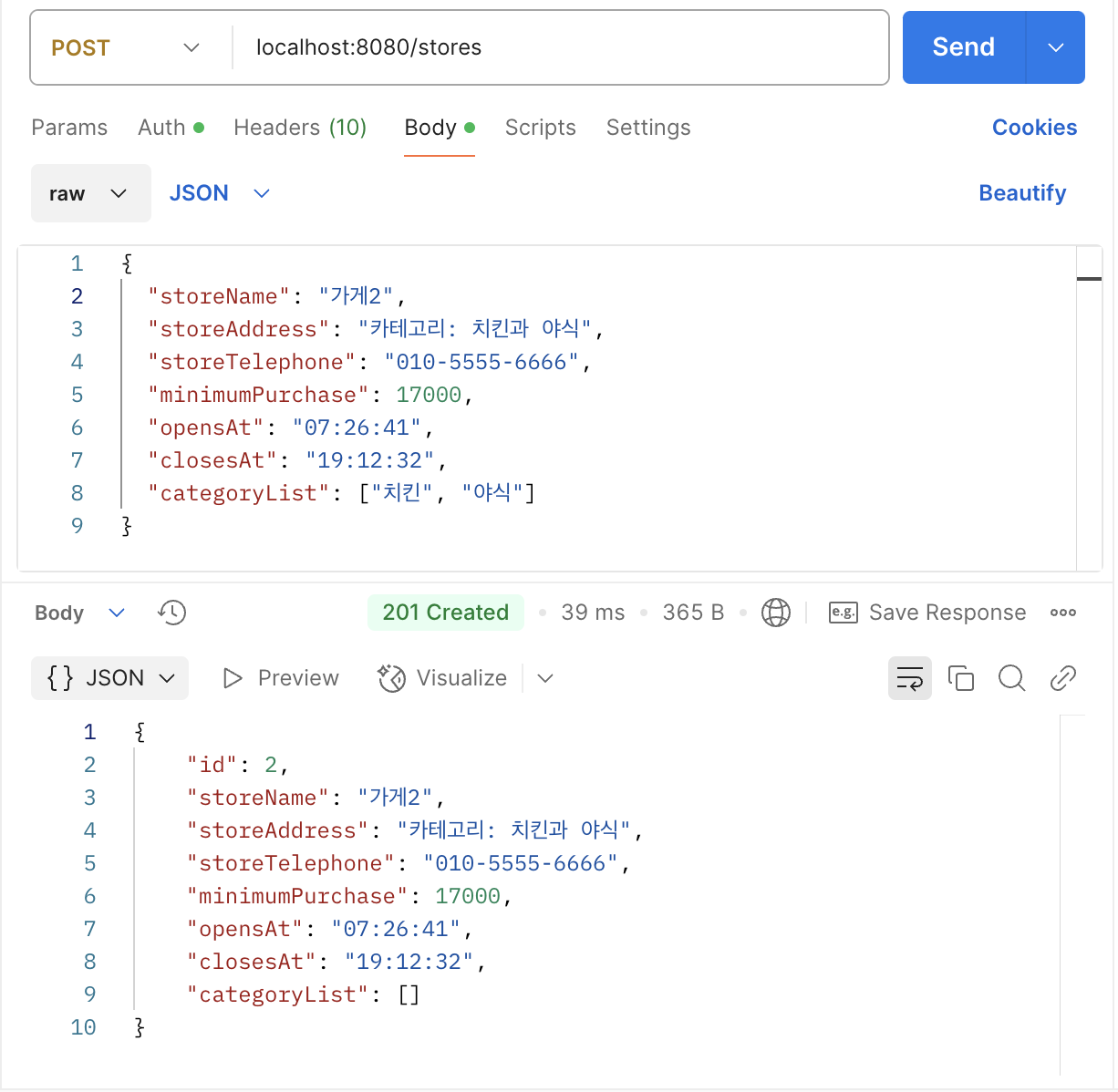
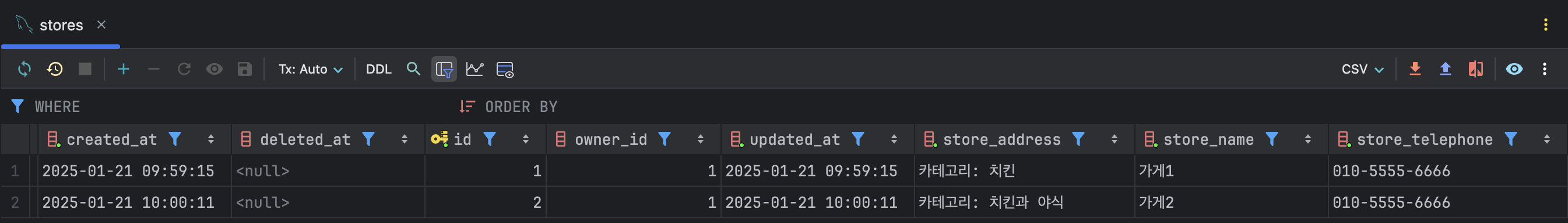
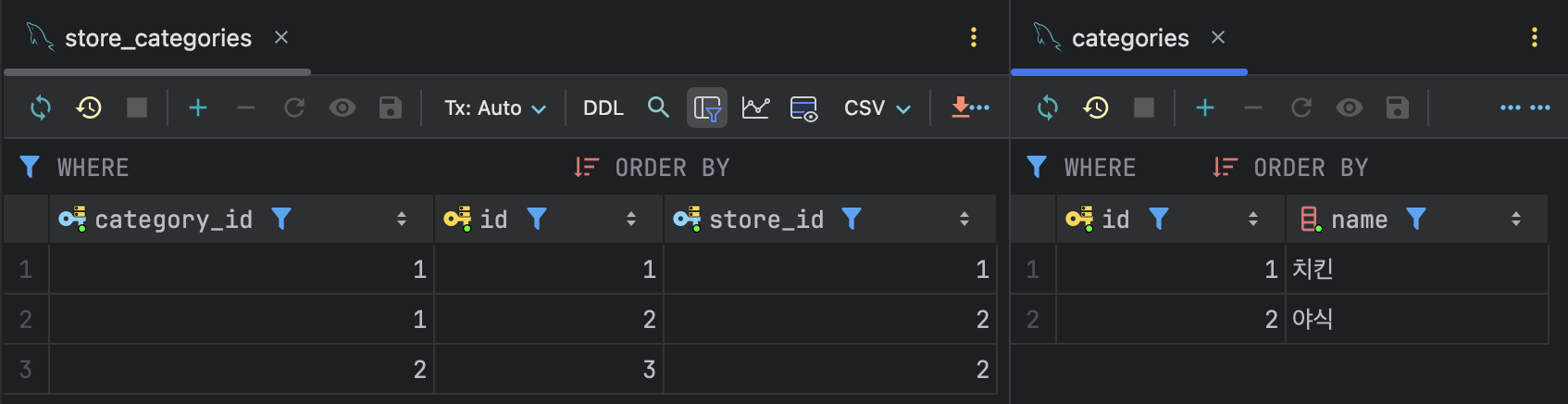
가게(Store), 카테고리(Category), 중간 테이블(Store Category)이 연관관계를 잘 맺었고 가게가 잘 생성되는지 확인했는데, 이상하게 입력된 카테고리가 데이터베이스(database)에만 저장되고 반환되지 않았다. 카테고리 목록을 제외한 여는 시간이나 주문 최소 금액 같은 다른 값은 모두 제대로 반환되었기 때문에, 혹시 응답 시 쓰는 DTO(Data Transfer Object)에 카테고리 목록이 들어가지 않았을지 모른다고 추측했다.
[원인 및 문제 해결 과정]
package com.example.outsourcingproject.store.service;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.auth.repository.OwnerAuthRepository;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.category.repository.CategoryRepository;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.entity.Category;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.entity.Owner;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.entity.Store;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.entity.StoreCategory;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.exception.badrequest.CategoryInvalidCountException;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.exception.badrequest.StoreInvalidCountExcessException;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.exception.notfound.OwnerNotFoundException;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.menu.repository.MenuRepository;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.store.dto.request.CreateStoreRequestDto;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.store.dto.response.CreateStoreResponseDto;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.store.repository.StoreCategoryRepository;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.store.repository.StoreRepository;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.utils.JwtUtil;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class StoreServiceImpl implements StoreService {
private final StoreRepository storeRepository;
private final OwnerAuthRepository ownerAuthRepository;
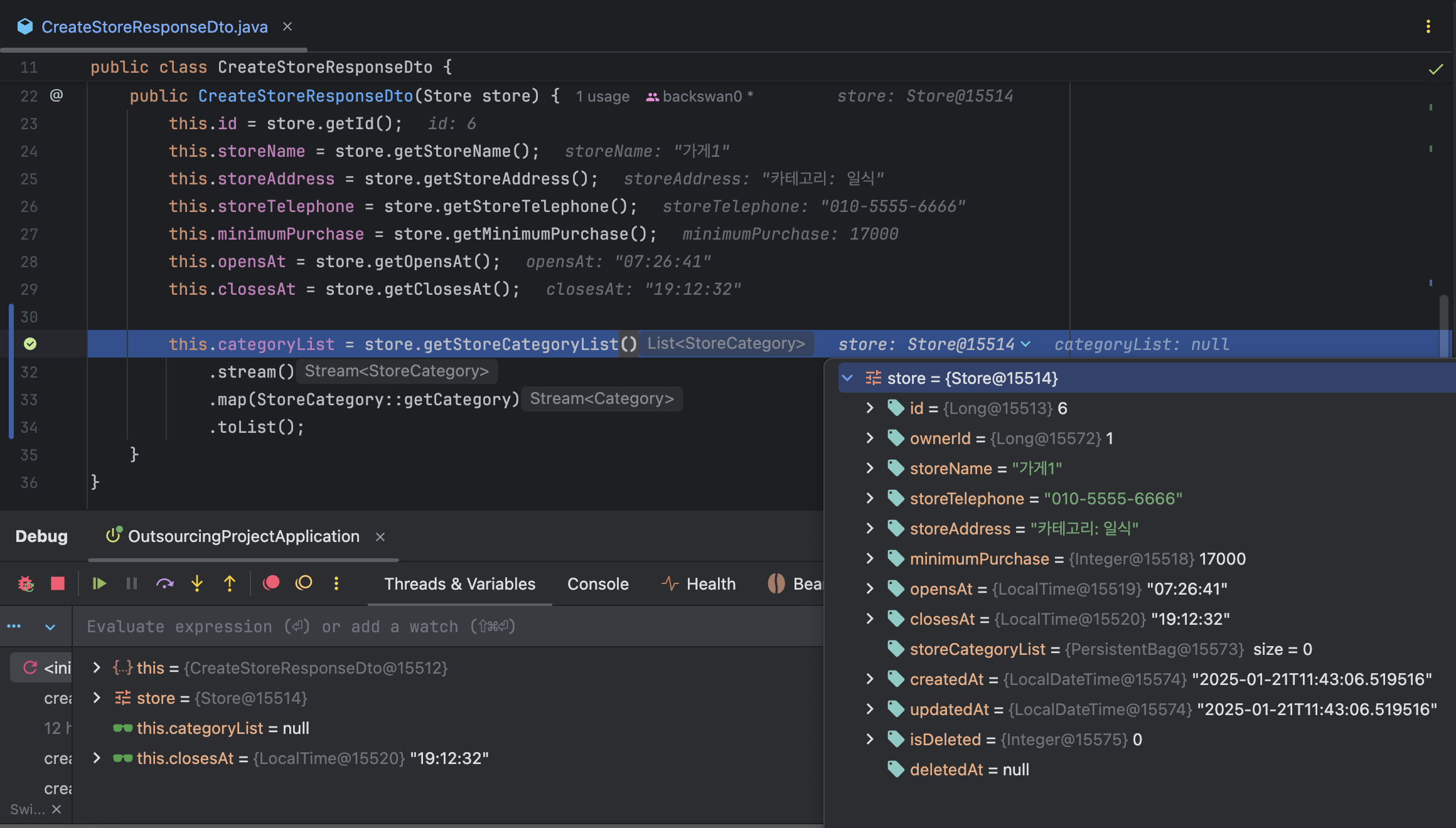
private final JwtUtil jwtUtil;
private final MenuRepository menuRepository;
private final CategoryRepository categoryRepository;
private final StoreCategoryRepository storeCategoryRepository;
@Transactional
@Override
public CreateStoreResponseDto createStore(
CreateStoreRequestDto requestDto,
String token
) {
String ownerEmail = jwtUtil.extractOwnerEmail(token);
Owner foundOwner = ownerAuthRepository.findByEmail(ownerEmail)
.orElseThrow(OwnerNotFoundException::new);
Long storeCount = storeRepository.countByOwnerIdAndIsDeleted(
foundOwner.getId(),
0
);
if (storeCount >= 3) {
throw new StoreInvalidCountExcessException();
}
Store storeToSave = new Store(
foundOwner.getId(),
requestDto.getStoreName(),
requestDto.getStoreAddress(),
requestDto.getStoreTelephone(),
requestDto.getMinimumPurchase(),
requestDto.getOpensAt(),
requestDto.getClosesAt()
);
Store savedStore = storeRepository.save(storeToSave);
List<Category> categoryList = new ArrayList<>();
categoryList = categoryRepository.findAllByNameIn(
requestDto.getCategoryList(),
Sort.unsorted()
);
if (categoryList.size() > 3) {
throw new CategoryInvalidCountException();
}
// 카테고리 목록을 StoreCategory 객체로 변환 및 저장 시작
List<StoreCategory> storeCategoryList = new ArrayList<>();
storeCategoryList = categoryList.stream()
.map(category -> new StoreCategory(
category,
savedStore
)
)
.toList();
storeCategoryRepository.saveAll(storeCategoryList);
// 카테고리 목록을 StoreCategory 객체로 변환 및 저장 종료
return new CreateStoreResponseDto(savedStore);
}
}원인은 역시 카테고리 목록이 중간 테이블인 Story Category에만 저장된다는 점에 있었다. 카테고리 목록은 가게 객체가 생성될 때 저장되지 않고 가게가 생성된 이후에 별도로 저장해야 했기 때문에, 생성자에서 처리하지 않고 메서드(method)를 별도로 만들어서 서비스 레이어(service layer)에서 해당 메서드를 호출했다.
package com.example.outsourcingproject.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityListeners;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import jakarta.persistence.OneToMany;
import jakarta.persistence.Table;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import lombok.Getter;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Comment;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.support.AuditingEntityListener;
@Entity
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
@Table(name = "stores")
@Getter
public class Store extends BaseEntity {
@Comment("가게 식별자")
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(columnDefinition = "BIGINT")
private Long id;
@Comment("사장님 식별자")
private Long ownerId;
@Comment("가게 이름")
@Column(
name = "store_name",
nullable = false
)
private String storeName;
@Comment("가게 전화번호")
@Column(
name = "store_telephone",
nullable = false
)
private String storeTelephone;
@Comment("가게 주소")
@Column(
name = "store_address",
nullable = false
)
private String storeAddress;
@Comment("주문 최소 금액")
@Column(
name = "minimum_purchase",
nullable = false
)
private Integer minimumPurchase;
@Comment("여는 시간")
@Column(
name = "opens_at",
nullable = false
)
private LocalTime opensAt;
@Comment("닫는 시간")
@Column(
name = "closes_at",
nullable = false
)
private LocalTime closesAt;
@Comment("가게 카테고리")
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "store")
private List<StoreCategory> storeCategoryList
= new ArrayList<>();
protected Store() {
}
public Store(
Long ownerId,
String storeName,
String storeAddress,
String storeTelephone,
Integer minimumPurchase,
LocalTime opensAt,
LocalTime closesAt
) {
this.ownerId = ownerId;
this.storeName = storeName;
this.storeTelephone = storeTelephone;
this.storeAddress = storeAddress;
this.minimumPurchase = minimumPurchase;
this.opensAt = opensAt;
this.closesAt = closesAt;
}
// [메서드 추가]
// (기능 1) 가게에 카테고리 목록 추가
// (기능 2) 가게와 카테고리 간 연관관계 설정
public void addStoreCategoryList(
List<StoreCategory> storeCategoryList
) {
this.storeCategoryList.addAll(storeCategoryList);
}
public void update(
String storeName,
String storeAddress,
String storeTelephone,
Integer minimumPurchase,
LocalTime opensAt,
LocalTime closesAt
) {
this.storeName = storeName;
this.storeAddress = storeAddress;
this.storeTelephone = storeTelephone;
this.minimumPurchase = minimumPurchase;
this.opensAt = opensAt;
this.closesAt = closesAt;
}
}// 사용 X
public void setStoreCategoryList (
List<StoreCategory> storeCategoryList
) {
this.storeCategoryList = storeCategoryList;
}// 사용 O
public void addStoreCategoryList(
List<StoreCategory> storeCategoryList
) {
this.storeCategoryList.addAll(storeCategoryList);
}처음에는 'Store Category 목록을 설정하는 기능'으로 메서드를 만들었는데, 이렇게 만든 메서드는 '세터(setter)'처럼 동작할 수밖에 없었다. 세터를 무분별하게 사용하면 코드의 의도가 불분명해지고, 언제든 외부에서 세터를 호출해서 객체 상태를 변경할 수 있기 때문에 객체의 일관성을 유지하기가 매우 어려웠다. 이런 이유로 기능을 '설정'이 아니라 '저장'으로 바꾸었고, 그 결과 'addStoreCategoryList'라는 이름과 그 행위가 일치하는 메서드를 만들 수 있었다.
package com.example.outsourcingproject.store.service;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.auth.repository.OwnerAuthRepository;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.category.repository.CategoryRepository;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.entity.Category;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.entity.Owner;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.entity.Store;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.entity.StoreCategory;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.exception.badrequest.CategoryInvalidCountException;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.exception.badrequest.StoreInvalidCountExcessException;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.exception.notfound.OwnerNotFoundException;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.menu.repository.MenuRepository;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.store.dto.request.CreateStoreRequestDto;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.store.dto.response.CreateStoreResponseDto;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.store.repository.StoreCategoryRepository;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.store.repository.StoreRepository;
import com.example.outsourcingproject.utils.JwtUtil;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class StoreServiceImpl implements StoreService {
private final StoreRepository storeRepository;
private final OwnerAuthRepository ownerAuthRepository;
private final JwtUtil jwtUtil;
private final MenuRepository menuRepository;
private final CategoryRepository categoryRepository;
private final StoreCategoryRepository storeCategoryRepository;
@Transactional
@Override
public CreateStoreResponseDto createStore(
CreateStoreRequestDto requestDto,
String token
) {
String ownerEmail = jwtUtil.extractOwnerEmail(token);
Owner foundOwner = ownerAuthRepository.findByEmail(ownerEmail)
.orElseThrow(OwnerNotFoundException::new);
Long storeCount = storeRepository.countByOwnerIdAndIsDeleted(
foundOwner.getId(),
0
);
if (storeCount >= 3) {
throw new StoreInvalidCountExcessException();
}
Store storeToSave = new Store(
foundOwner.getId(),
requestDto.getStoreName(),
requestDto.getStoreAddress(),
requestDto.getStoreTelephone(),
requestDto.getMinimumPurchase(),
requestDto.getOpensAt(),
requestDto.getClosesAt()
);
Store savedStore = storeRepository.save(storeToSave);
List<Category> categoryList = new ArrayList<>();
categoryList = categoryRepository.findAllByNameIn(
requestDto.getCategoryList(),
Sort.unsorted()
);
if (categoryList.size() > 3) {
throw new CategoryInvalidCountException();
}
// 카테고리 목록을 StoreCategory 객체로 변환 및 저장 시작
List<StoreCategory> storeCategoryList = new ArrayList<>();
storeCategoryList = categoryList.stream()
.map(category -> new StoreCategory(
category,
savedStore
)
)
.toList();
// 카테고리 목록을 StoreCategory 객체로 변환 및 저장 종료
storeCategoryRepository.saveAll(storeCategoryList);
// [addStoreCategoryList 메서드 호출]
savedStore.addStoreCategoryList(storeCategoryList);
return new CreateStoreResponseDto(savedStore);
}
}위와 같이 코드를 추가한 다음에 애플리케이션을 다시 실행했다. 오류가 해결되었기를 마음속으로 빌고 또 빌면서.
그 결과…….
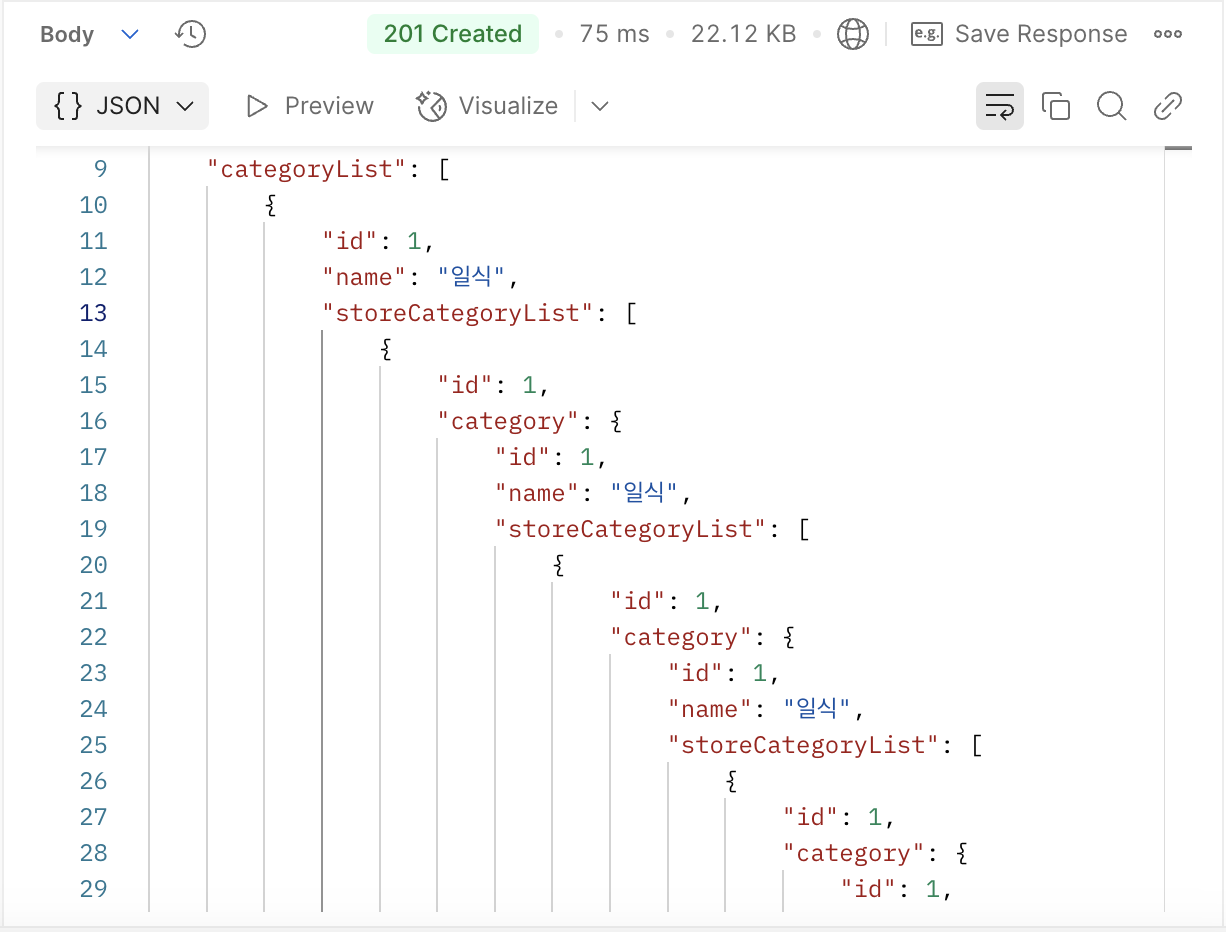
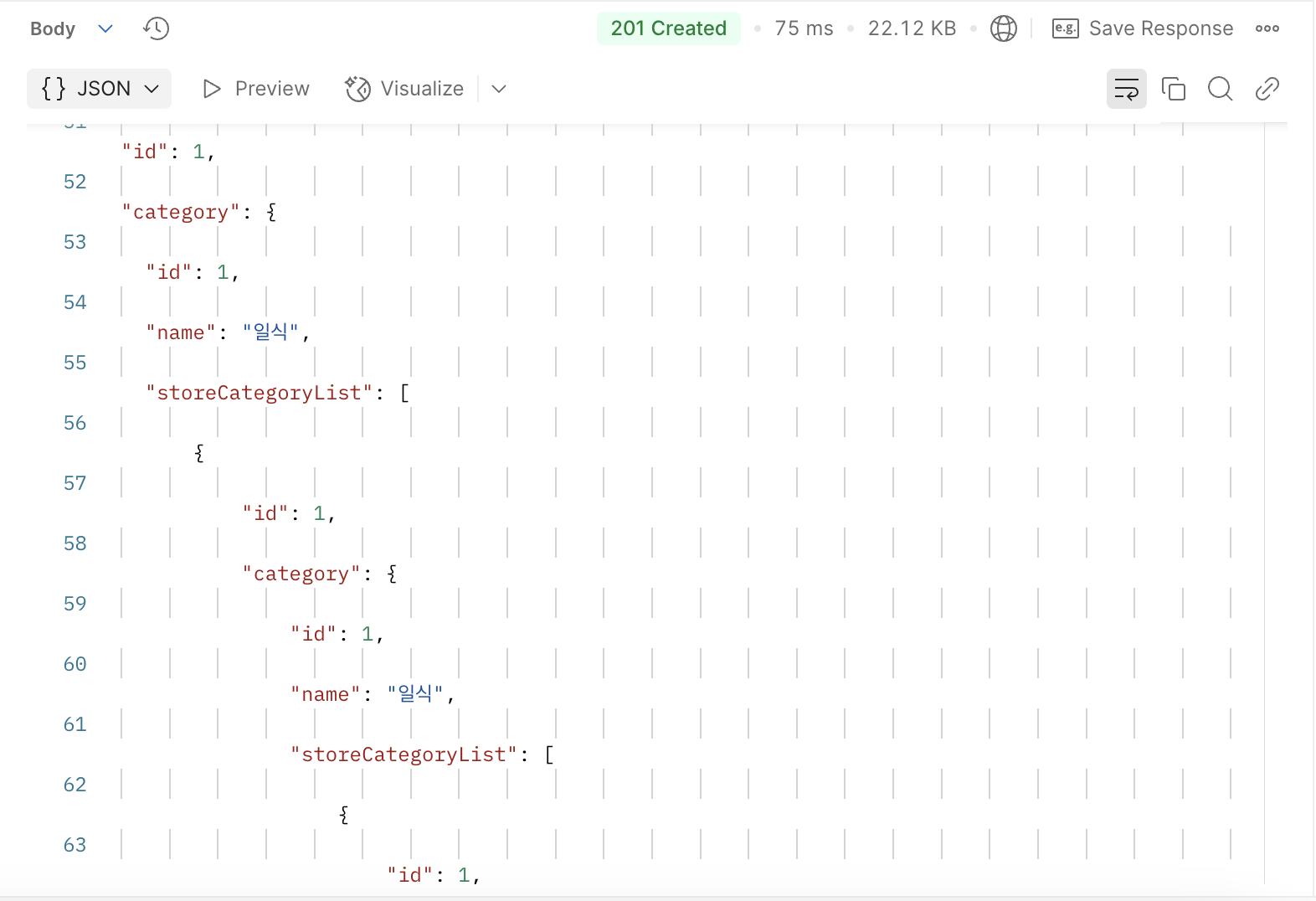
순환 참조에 제대로 걸렸다.
과장이 아니라 진짜 '이게 뭐지? 꿈인가?' 싶었다.
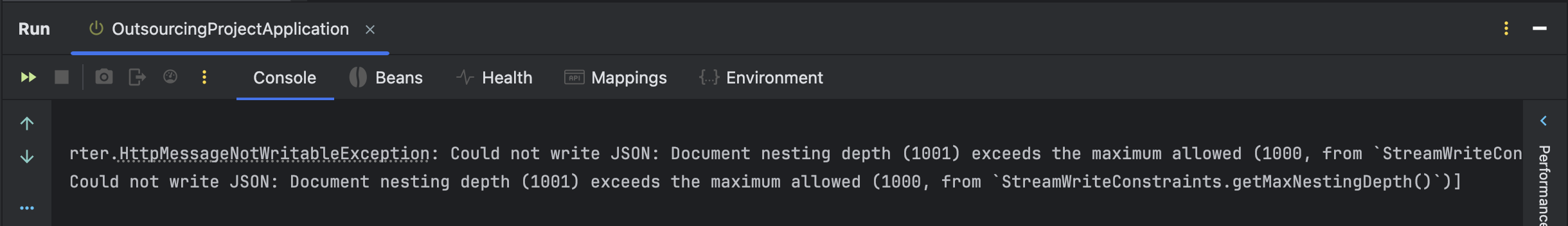
HttpMessageNotWritableException:
// (1) JSON으로 직렬화할 수 없는 예외 발생
Could not write JSON:
// (2) JSON을 직렬화할 수 없음
Document nesting depth (1001) exceeds the maximum allowed
// (3) JSON 객체의 중첩 깊이(1001)가 허용된 최대 깊이(1000)를 초과함
// 1001: 객체 안에 객체가 있고, 또 그 안에 객체가 있는 구조일 때의 깊이
// == 객체가 중첩된 깊이
(1000, from `StreamWriteConstraints.getMaxNestingDepth()`)
// (4) 1000: JSON의 최대 중첩 깊이
// `StreamWriteConstraints.getMaxNestingDepth()`에서 정의됨
// Jackson 라이브러리에서는 보통 1000으로 설정
// 해당 값을 초괴하면 HttpMessageNotWritableException 발생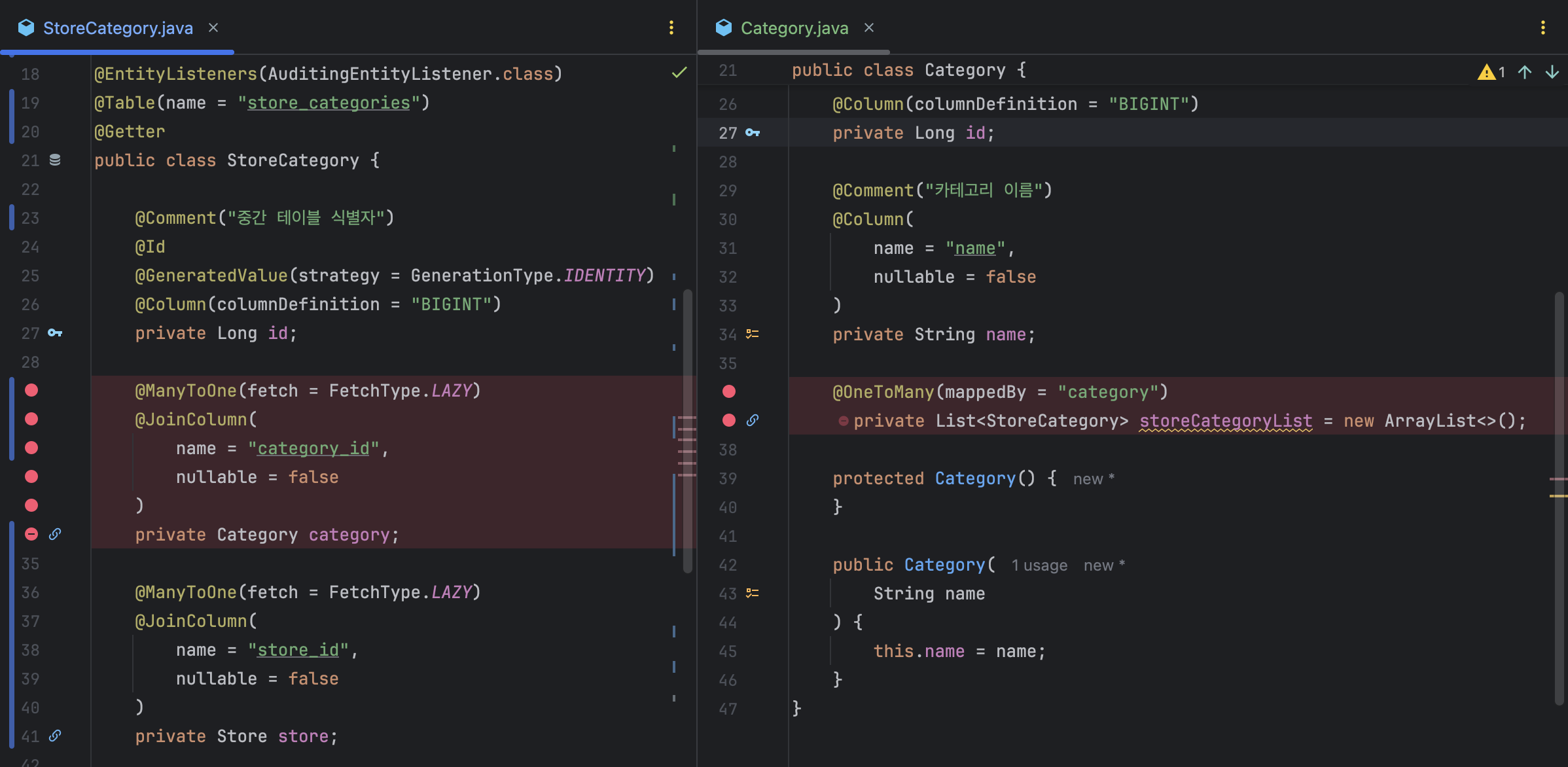
예외 메시지를 보고 추측할 수 있다시피, StoreCategory와 Category라는 두 객체가 양방향으로 연관관계를 맺어서 각 객체가 직렬화되어 반환되며 순환 참조에 빠지고 말았다. category 객체 안에 storeCategoryList 객체가 있고, storeCategoryList 안에 category가 있으며, 그 안에도 다시 storeCategoryList가 포함되어서 서로를 계속 참조하는 구조가 되어 무한히 직렬화되며 순환 참조 문제가 발생했다.
'category → storeCategoryList → category → storeCategoryList → category …….'
이런 식으로 말이다.
순환 참조 문제를 해결하려면 첫째, Category 객체를 직접 반환하지 않고 필요한 정보만 담은 DTO로 반환하거나 둘째, @JsonManagedReference 같은 어노테이션(annotation)을 붙여서 직렬화 대상에서 제외해야 했다.
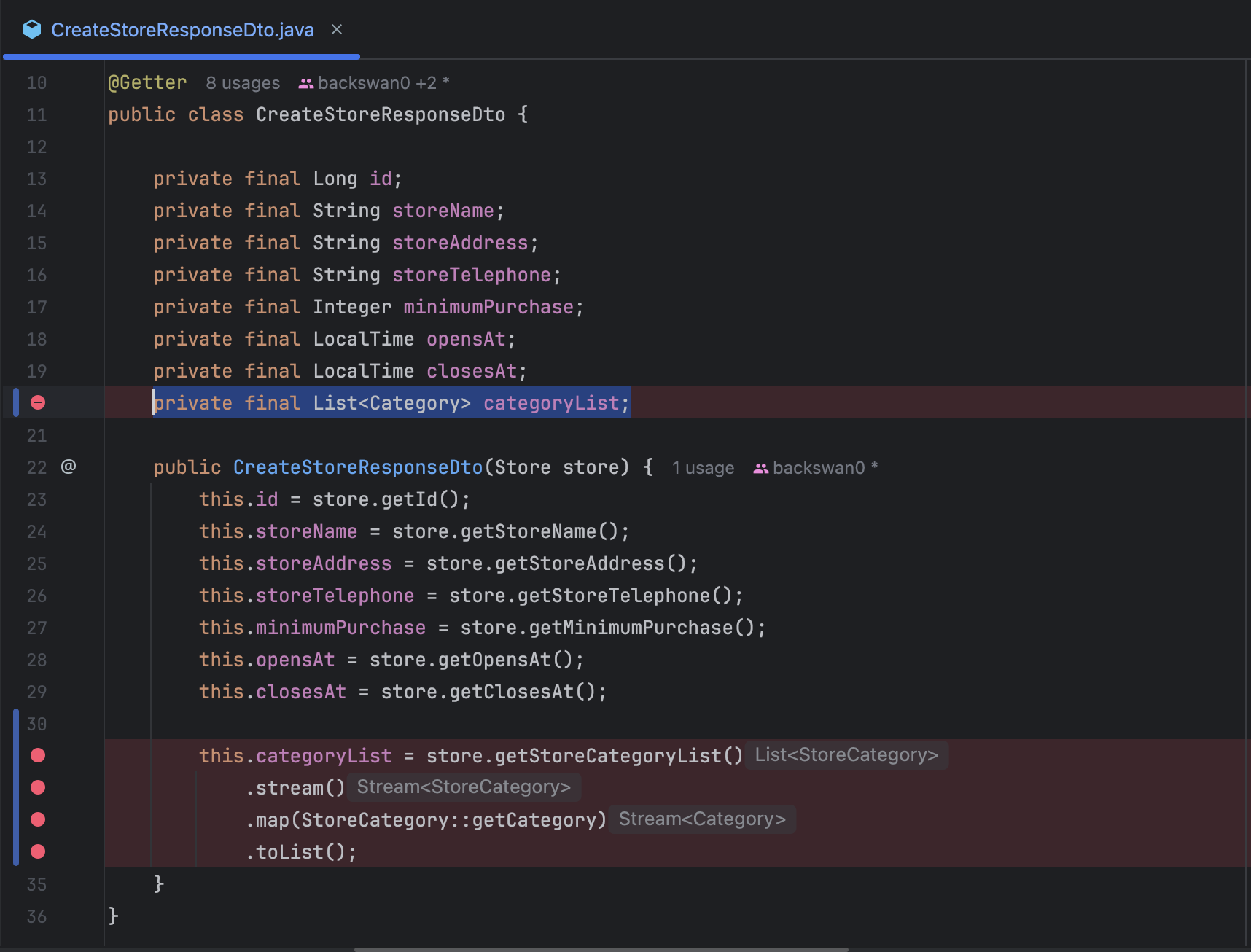
일단 다른 정보는 DTO로 잘 반환해 놓고, categoryList만 DTO가 아닌 객체로 직접 반환하려고 했다는 점이 어처구니없었지만, 두 가지 해결책 외에도 또 다른 질문이 머릿속을 맴돌았다.
'Store Category와 Category 객체가 꼭 양방향으로 연관되어야 하나?'
'두 객체가 항상 함께 조회, 수정, 삭제될 필요가 있을까?'
'Store와 Store Category는 함께 저장되고 조회되어야 하지만, Category는 자신이 어느 가게와 연결되었는지 꼭 알아야 할까?'
양방향 연관관계는 한 객체를 수정했을 때 다른 객체도 함께 영향받는 등 의도치 않은 동작이 발생할 수 있어서, 꼭 필요할 때가 아니라면 단방향 연관관계를 설정하는 편이 바람직했다. 이런 이유로 Store와 Store Category를 단방향 연관관계로 설정하기로 했다.
[해결]
'Troubleshooting: 무엇이 문제였는가? > 플러스 프로젝트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 10단계: "NoSuchBeanDefinitionException - No qualifying bean of type 'JwtUtil' available" (0) | 2025.01.28 |
|---|---|
| 10단계: Cannot invoke "Object.getClass()" because "constant" is null (0) | 2025.01.20 |
| 10단계: Null이 아니라 널 보고 싶어요, 이메일 씨 (0) | 2025.01.20 |